

 about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
Quick Links
Featured Citations
Running a genetic stop sign accelerates oxygen metabolism and energy production in horses. Castiglione GM, Chen X et al. Science. 2025 Mar 28;387(6741):eadr8589.
Structure and mechanism of the Zorya anti-phage defence system. Hu H, Popp PF et al. Nature. 2025 Mar 27;639(8056):1093-1101.
Genomic and structural insights into Jyvaskylavirus, the first giant virus isolated from Finland. Almeida GMF, Arriaga I et al. eLife. 2025 Mar 25;13:RP103492.
In-cell architecture of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Waltz F, Righetto RD et al. Science. 2025 Mar 21;387(6740):1296-1301.
Structure and mechanism of vitamin-K-dependent γ-glutamyl carboxylase. Wang R, Chen B et al. Nature. 2025 Mar 20;639(8055):808–815.
More citations...News
March 19, 2025

|
March 1, 2025
 Follow UCSF ChimeraX on BlueSky!
@chimerax.ucsf.edu
Follow UCSF ChimeraX on BlueSky!
@chimerax.ucsf.edu
December 25, 2024

|
Upcoming Events
UCSF ChimeraX (or simply ChimeraX) is the next-generation molecular visualization program from the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics (RBVI), following UCSF Chimera. ChimeraX can be downloaded free of charge for academic, government, nonprofit, and personal use. Commercial users, please see ChimeraX commercial licensing.
ChimeraX is developed with support from National Institutes of Health R01-GM129325.
 ChimeraX on Bluesky:
@chimerax.ucsf.edu
ChimeraX on Bluesky:
@chimerax.ucsf.edu
Feature Highlight

Hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) can be identified with the
H-Bonds tool,
hbonds command,
or the
Molecule Display
icon
![]() and plotted as an interactive histogram with the command
crosslinks
histogram.
and plotted as an interactive histogram with the command
crosslinks
histogram.
The ChimeraX graphics window shows the complex between a natural killer cell receptor 2B4 and its ligand CD48 (PDB 2ptt). The receptor protein is blue, the ligand protein pink, and H-bonds between them dashed yellow, with H-bonding residues labeled. Although not done here, the H-bonds could also be labeled by distance.
The histogram of H-bond distances on the top right is interactive: when the cursor is placed over a bar in the histogram, the corresponding H-bonds are temporarily enlarged in the 3D view and the others hidden. For image setup other than orientation, see the command file hb3.cxc.
More features...
Example Image
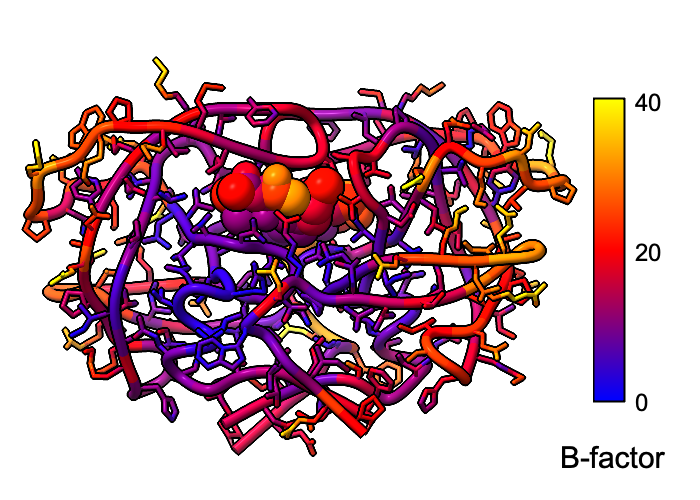
Atomic B-factor values are read from PDB and mmCIF input files and assigned as attributes that can be shown with coloring and used in atom specification. This example shows B-factor variation within a structure of the HIV-1 protease bound to an inhibitor (PDB 4hvp). For complete image setup, including positioning, color key, and label, see the command file bfactor.cxc.
Additional color key examples can be found in tutorials: Coloring by Electrostatic Potential, Coloring by Sequence Conservation
About RBVI | Projects | People | Publications | Resources | Visit Us
Copyright 2018 Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.